
[Physical Features of India] The Peninsular Plateau Class 9 Teachoo
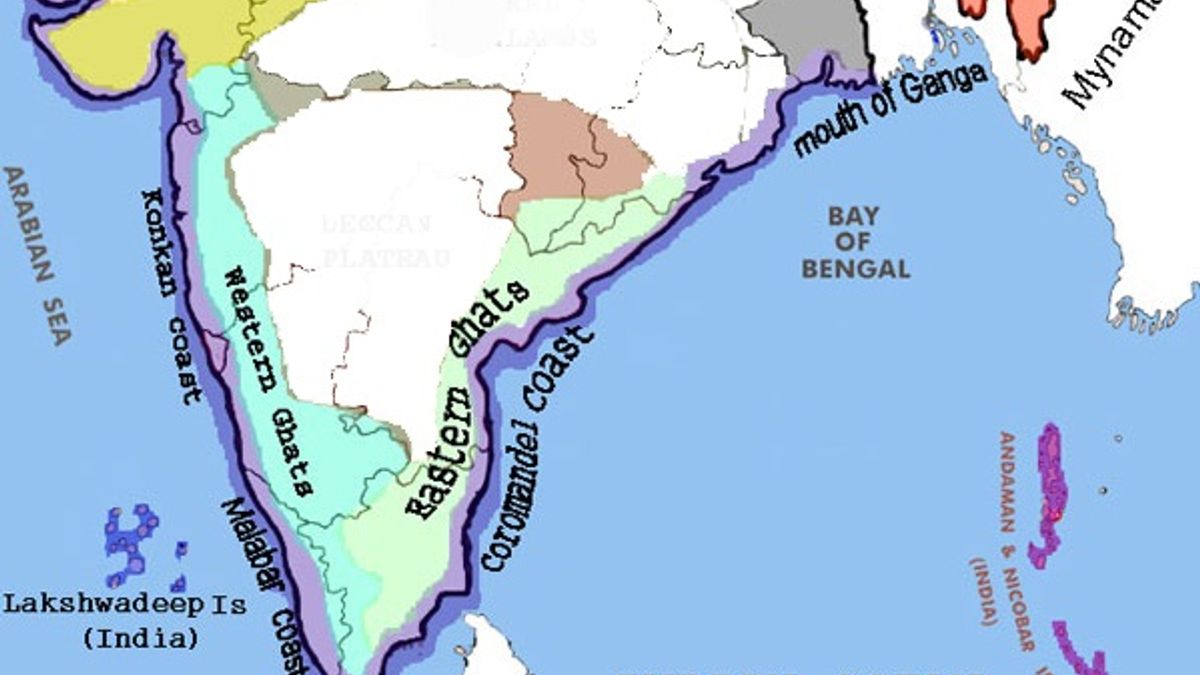
The Western Ghats of India, also known as the Sahyadri Hills is a range of mountains that runs parallel to the western coast of the Indian Peninsular region. The Western Ghats stretches for about 1600 km from the Tapi river in the North to Kanyakumari in the South and its width varies from 50 to 80 km.

Report of the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel Part I 2. Introduction, 3. Mandate of the
The Western Ghats in Matheran, Maharashtra, India. Western Ghats, north-south-running range of mountains or hills in western India that forms the crest of the western edge of the Deccan plateau parallel to the Malabar Coast of the Arabian Sea. The Western Ghats are a biodiversity hot spot, a biologically rich but threatened region, and a.

Eastern Ghats On Indian Map
In India, L. t. malabaricus Wroughton, 1917 inhabits the wet forests of the Western Ghats, and L. t. lydekkerianus Cabrera, 1908 is found in the relatively dry shrub jungles of the Eastern Ghats.
Eastern And Western Ghats Map Cape May County Map
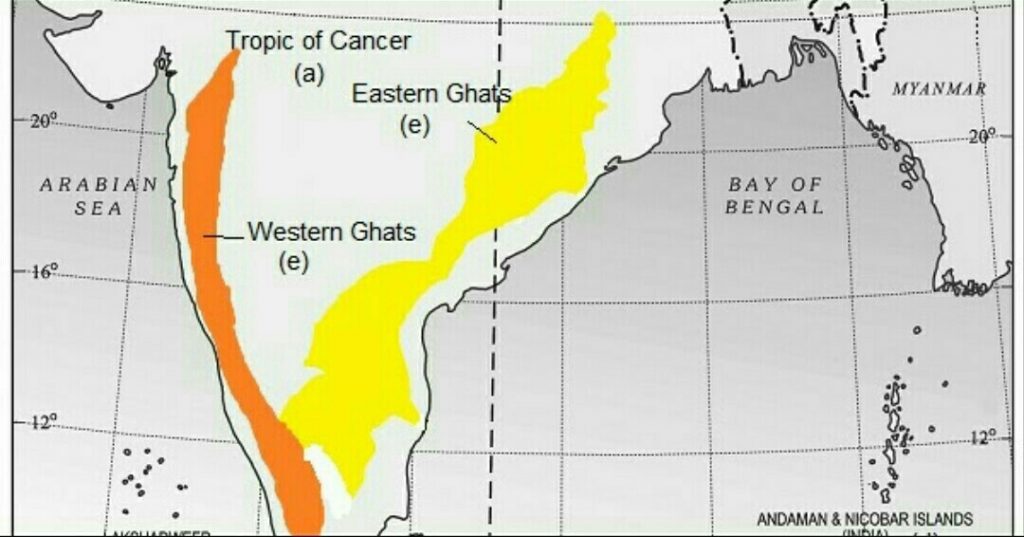
The Western Ghats, also known as the Sahyadri range, is a chain of mountains that runs parallel to India's western coast. The Eastern Ghats, on the other hand, is a series of hills and mountains that run along India's eastern coast.. Map of Eastern Ghat. Elevations. Another difference between the two mountain ranges is their elevation.

27 Western Ghats On Map Maps Online For You
India Geographical Map The Peninsular region of India is characterized by its hills. The Western Ghats, which run along the coastline of the Arabian Sea, are a series of mountains that rise up to 2,695 meters and form a natural boundary between the coastal plain and the Deccan Plateau. To the east, the Eastern Ghats […]

Western Ghats Mountains, Definition, & Description Britannica
Ghats, two mountain ranges forming the eastern and western edges, respectively, of the Deccan plateau of peninsular India.The two ranges run roughly parallel to the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea coasts, respectively, from which they are separated by strips of fairly level coastal land. In Hindi ghat means "river landing stairs" or "mountain pass" and has been extended in its Anglicized.

Eastern Ghats Map
Maps. Date. Title. 2012. Western Ghats - Inscribed Property. Disclaimer. The Nomination files produced by the States Parties are published by the World Heritage Centre at its website and/or in working documents in order to ensure transparency, access to information and to facilitate the preparations of comparative analysis by other nominating.

Map showing the Eastern and Western Ghats, the Mysore Plateau and the... Download Scientific
Nilgiri hills in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. Anaimalai Hills and Cardamom hills in Kerala. 2. The Western Ghats is an elevated and continuous range of mountains. 3. The average elevation of Western Ghats is about 1,500 m. 4. Western Ghat is the origin of various Peninsular rivers.
Tabulate the difference between western ghats and eastern ghats? Andhra Pradesh PCS Exam Notes
The Deccan plateau is one of India's primary landmasses and one of the country's physiographic divisions. It is bounded on the west by the Western Ghats and on the east by the Eastern Ghats. The Western Ghats run parallel to the shore. They are unbroken and can only be traversed through passes. The Eastern Ghats are dissected by rivers that flow into the Bay of Bengal, making them.

Eastern Ghats In India Map Share Map
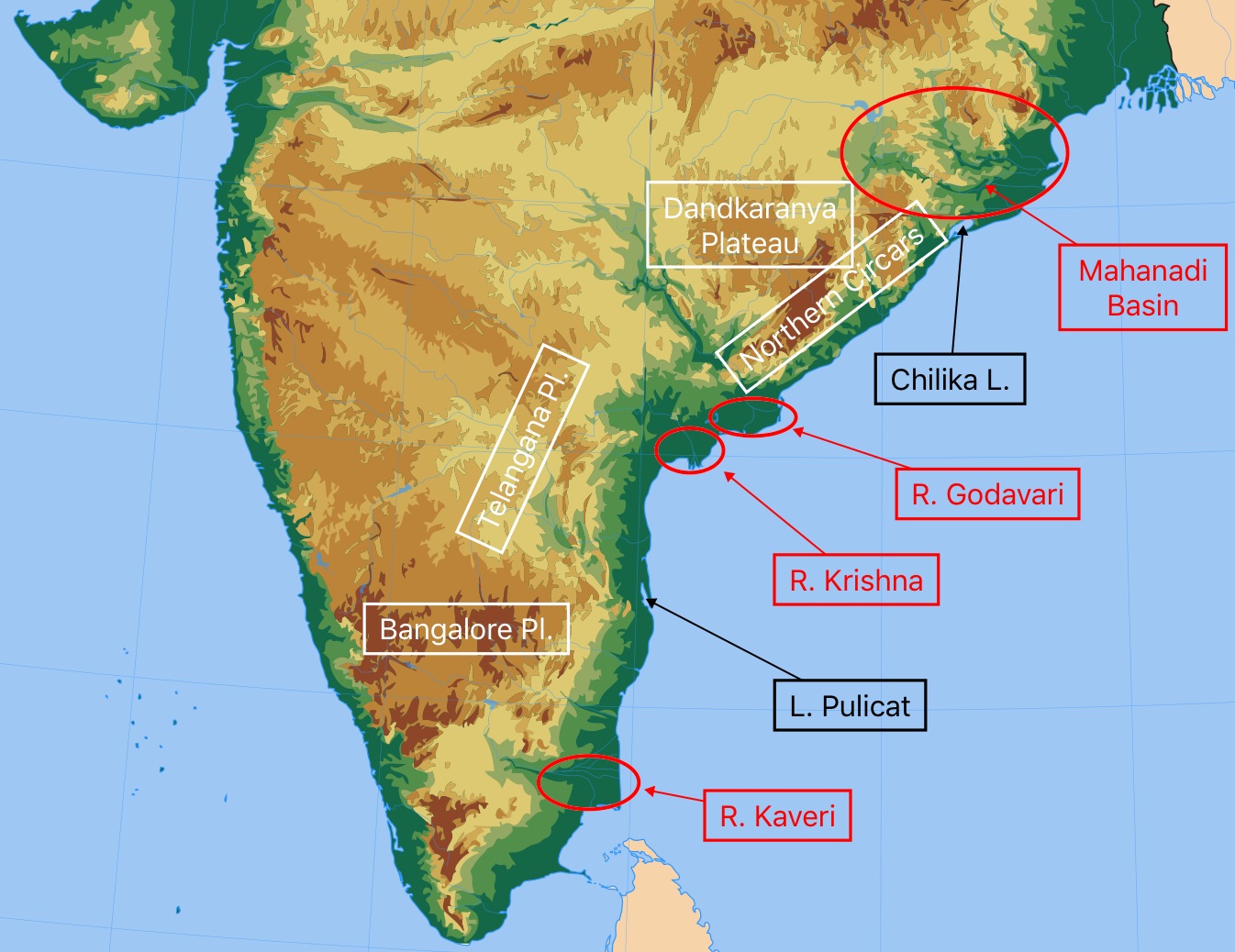
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through the states of Odisha and Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu by, passing parts of Karnataka and Telangana on the way. They are eroded and cut through by four major rivers of peninsular India, viz., the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri. Sitamma Konda is the highest point in both.

Western and eastern ghats on political map of india Brainly.in
The highest point in Odisha is Deomali, which is 1672 metres high. With a height of 1680 metres, Arma Konda/Jindhagada Peak is Andhra Pradesh's highest point. The BR hill range in Karnataka is the tallest in the Eastern Ghats, with many of its peaks rising beyond 1750 metres. The tallest mountain in the Eastern Ghats is Kattahi Betta in the.

Eastern Ghats Map
Rivers These Ghats act as a barrier for the rain-laden south-west monsoon winds, thus, making the Western Ghats the main watershed of Peninsular India. It receives an annual rainfall of between.
The Western Ghats And Eastern Ghats UPSC
The Western Ghats is an "Evolutionary Ecotone" illustrating "Out of Africa" and "Out of Asia" hypotheses on species dispersal and vicariance. [tb1] Criterion (x): The Western Ghats contain exceptional levels of plant and animal diversity and endemicity for a continental area. In particular, the level of endemicity for some of the 4.
eastern ghats Liberal Dictionary
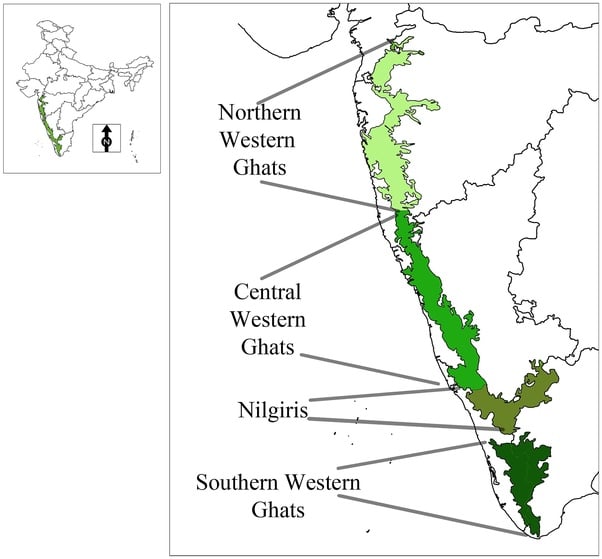
The Western Ghats, also known as the Sahyadri mountain range, is a mountain range that covers an area of 160,000 km 2 (62,000 sq mi) in a stretch of 1,600 km (990 mi) parallel to the western coast of the Indian peninsula, traversing the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the 36 biodiversity hotspots in the world.
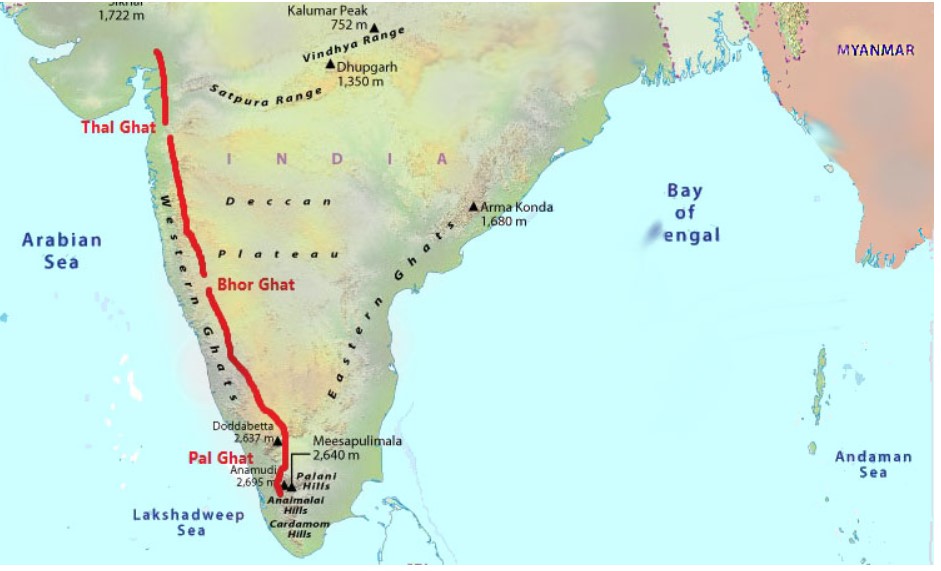
Physiography of India Important Ghats of India
These hills cover 160,000 km² (roughly 6% of India's total geographical area) and form the catchment area for complex riverine drainage systems that drain almost 40% of India. The average elevation is around 1,200-1300 metres. The Western Ghats are home to 30% of flora and fauna species found in India. 39 Western Ghats series sites were.
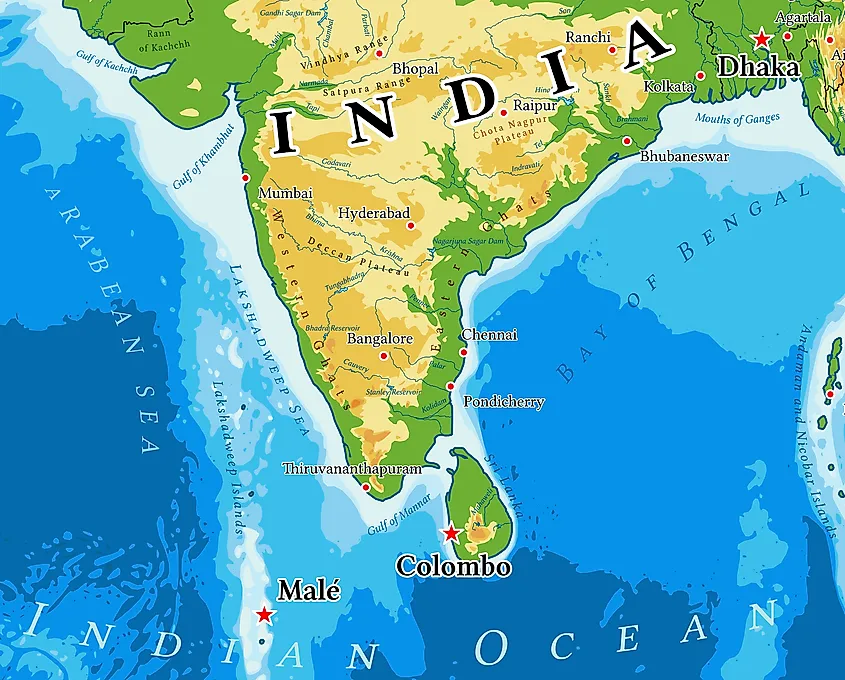
Western Ghats Mountains Map
The Vavul Mala (2,339 m), the Kudremukh (1,892 m) and Pashpagiri (1,714 m) are important peaks. The Nilgiri Hills which join the Sahyadris near the trijunction of Karnataka, Kerala and TN, rise abruptly to over 2,000 m. They mark the junction of the Western Ghats with Eastern Ghats. Doda Betta (2,637 m) and Makurti (2,554 m) are important peaks.